
This holds the new ligament in place.Īt the end of the surgery, your surgeon will close your cuts with sutures (stitches) and cover the area with a dressing.
Your surgeon will attach the new ligament to the bone with screws or other devices to hold it in place. This new tissue will be put at the same place as your old ACL. Your surgeon will make tunnels in your bone to bring the new tissue through. Then, the autograft will be removed through this cut. If your own tissue is being used to make your new ACL, your surgeon will make a larger cut. The torn ligament will be removed with a shaver or other instruments. Your surgeon will fix any other damage found, and then will replace your ACL by following these steps: Your surgeon will make other small cuts around your knee and insert other medical instruments. Your surgeon will use the camera to check the ligaments and other tissues of your knee. The camera is connected to a video monitor in the operating room. With arthroscopy, a tiny camera is inserted into the knee through a small surgical cut. The procedure is usually performed with the help of knee arthroscopy. Tissue taken from a donor is called an allograft. Your hamstring are the muscles behind your knee. The two most common places to take tissue from are the knee cap tendon or the hamstring tendon. Tissue taken from your own body is called an autograft. A donor is a person who has died and chose to give all or part of their body to help others. The tissue to replace your damaged ACL will come from your own body or from a donor. Other kinds of anesthesia, like regional anesthesia or a block, may also be used for this surgery. 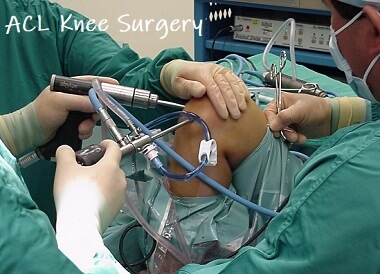
This means you will be asleep and pain-free.

Most people have general anesthesia right before surgery.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
